Description
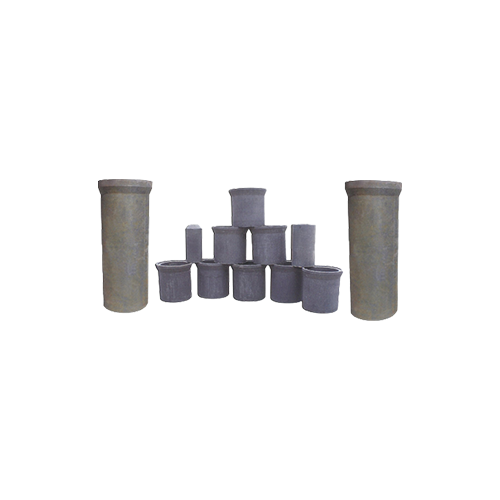
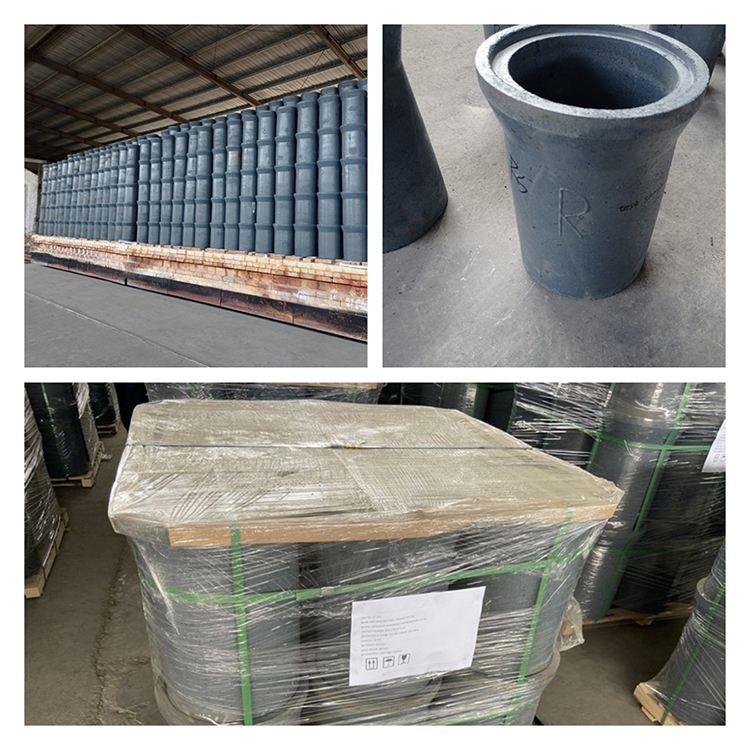
Crucibles comprise primarily silicon carbide crucibles and graphite crucibles, both crafted from materials like flake graphite and silicon carbide. These crucibles exhibit several notable features, including efficient thermal conductivity, substantial density, resistance to corrosion, minimal slag adherence, elevated mechanical strength, resilience to oxidation, and capacity for thermal shock resistance. Importantly, they remain inert in the presence of molten metals during the smelting process, mitigating leakage and adhesion concerns. These crucibles find extensive application in alloy tool steel smelting and the non-ferrous metal smelting of copper, aluminum, and related alloys.

Technique Data
| Item | Molten copper, precious metals and rare earth alloys | Molten aluminum and low melting point metals | ||
| Forming method | Plasticity | Isostatic pressure | Plasticity | Isostatic pressure |
| Carbon Content % | ≥38 | ≥45 | ≥38 | ≥45 |
| Bulk density g/cm3 | ≥1.7 | ≥1.85 | ≥1.7 | ≥1.85 |
| Apparent porosity % | ≤29 | ≤21 | ≤29 | ≤21 |
| Cold Crushing Strength MPa | ≥20 | ≥25 | ≥20 | ≥25 |
| Refractoriness ℃ | ≥1500 | ≥1500 | ≥1400 | ≥1400 |